At the moment when the dividend of domestic Internet has peaked, more and more Chinese entrepreneurs and investors have begun to pay attention to "globalization". In 2021, 36 krypton will go to seaContinue to launch globalization manualTo explain the basic features, cultural environment, market characteristics and entrepreneurial opportunities of Germany, France, Britain, Italy and other European countries one by one. In turnGermany、FranceandbritainLater, we turned our attention to Italy in southern Europe,In the first part, we took the reader "into" Italy by reviewing the history and telling the humanitiesIn this chapter, we will focus on the Italian venture capital market to explore the opportunities and challenges of the "Kingdom of SMEs".
Venture Capital Ecology
Italy is a developed industrial country and one of the four largest economies in Europe. Manufacturing, agriculture and service industries are its pillar industries, among which the service industry accounts for about 70% of the country's gross domestic product (GDP). The economic gap between the north and the south in the country is large. The industry and commerce in the north is developing rapidly, while the south focuses on agricultural development. In addition, Italy has a special business structure, with small and medium-sized enterprises accounting for more than 90% of the total number of enterprises, which can be called the "kingdom of small and medium-sized enterprises".
From the perspective of venture capital environment, Italy's entrepreneurial environment is still in a relatively early stage, still facing high taxes, imperfect judicial supervision system and low implementation efficiency. The investment environment has developed rapidly in 2020. It is reported that Italian start-ups will raise 569 million euros in 2020, a year-on-year increase of 55%, the best result in five years.
industrial structure
When it comes to industrial structure, there is a big difference in the industrial development between the south and the north of Italy. The industry and commerce in the north are very developed, while the south mainly develops agriculture. In addition, the service industry is now one of the most important industries in the country.
In terms of industry, it is understood that in the 1950s, Italy (especially the northern region) began to promote the development of industrialization. After the technical reform in the 1980s, Italy's jewelry, leather products, textiles, clothing manufacturing, furniture, machinery manufacturing and other industries began to develop at a high speed. At the same time, the huge demand for labor also made more people choose to engage in related industries, A large number of highly specialized talents have been further cultivated.
Italy is not only a major manufacturer of luxury brands such as clothing and jewelry, but also has nearly a quarter of the world's fashion brands. It also has outstanding strength in aerospace, automobile manufacturing, robot, machine tool manufacturing, mechanical equipment, military industry and other fields. Taking the world famous automobile manufacturing as an example, the country has a very complete automobile manufacturing industry chain, which is very comprehensive from design to production and sales. Ferrari, Lamborghini, Bugatti Veyron and other super sports cars all come from Italy. In addition, the density of industrial robots in Italy is very high, ranking second in Europe, and the export scale of industrial robots ranks fifth in the world, which is enough to compete with Japan and Germany.

In terms of agriculture, Italy is a large agricultural country, and the agriculture in the south of the country is very developed. According to statistics, Italy has nearly 2 million farms, of which more than 60% are located in the south. As there are many hills in Italy, the land is very scattered and there are few large farms. Influenced by the measures of redistributing land and promoting the effective use of land in the Land Reform Law issued in 1950, Italian agriculture began to develop rapidly. In recent years, Italy's agricultural GDP ranks first in the EU. However, affected by the epidemic, according to the data of the Italian Bureau of Statistics, Italy's agricultural output will decline by 3.3% in 2020, of which olive oil will decline by 18%, cash crops will decline by 2.2%, and wine will decline by 1.9%; The added value of agriculture dropped to 31.3 billion euros, still ranking first in the European Union, but down 6.1% over the previous year.
In terms of service industry, the service industry in this country is a continuously growing industry. In 2020, 68% of Italians will be engaged in the service industry, which accounts for about 70% of the country's GDP. Among them, the banking industry, which flourished in the Middle Ages, is still an important part of the Italian economy. In addition, Italy's tourism industry is also very developed, and the country has 57 world heritage sites. In 2018, Italy's tourism industry developed rapidly, receiving more than 420 million foreign tourists throughout the year, a record high. However, the impact of the epidemic has caused the country's tourism industry to "go back 30 years". According to the report released by the Italian Tourism Federation, the number of international tourists arriving in Italy will decrease by 78 million in 2020, the number of tourists will decrease by 240 million, and the number of Italian citizens traveling abroad will decrease by 36 million. Italy's tourism industry has returned to its level 30 years ago.
Entrepreneurship environment
Speaking of Italy's entrepreneurial environment, compared with Britain, which has a very good business environment, Italy's entrepreneurial environment is still in the early stage of "becoming perfect". Next, let's analyze the opportunities and challenges in Italy's entrepreneurial environment.
From the perspective of advantages, first of all, Italy has geographical advantages. Located in the center of the Mediterranean Sea, Italy is an important hub connecting Southern Europe, Central and Eastern Europe, North Africa and the Middle East. 20% of the world's sea transportation, 30% of fuel transportation and 25% of container transportation all pass through Italian ports. As a member of the European Union, Italian enterprises can enter more than 30 countries in the European Economic Area duty-free.
Secondly, in order to gain the trust of more entrepreneurs and investors, Italy has revised relevant laws and regulations in privatization, market opening and reduction of restrictions. At the same time, it has reformed the financial market and the government's public administration mechanism, making the country's market management more transparent and open.
Third, Italy is one of the largest manufacturing countries in Europe, second only to Germany. The products made in Italy enjoy the reputation of "high quality and design". Entrepreneurs can find a large number of professionals in different fields, such as fashion products, textiles, industrial machinery, metals, chemicals, food, automobiles and pharmaceuticals.
Fourth, Italy has a very strong innovation ability and awareness. It is understood that Italy spends more than 25 billion euros on R&D every year, making it the fourth highest R&D investment country in Europe. Among them, the country's biotechnology, chemical agents, aerospace and other high-tech fields are in the forefront of Europe. At the same time, Italy is building a network of innovation incubators and science and technology parks, many of which are cooperating with universities and local training institutions to ensure the supply of talents.
Despite the above advantages, people who start businesses in Italy still need to face the following challenges.
First, high taxes. It is understood that Italy is a high tax country, and its corporate tax burden is one of the most "heavy" in European countries. According to the Business Environment Report issued by the World Bank, in Italy, enterprises must pay 14 taxes every year, including corporate income tax (IRES), regional production tax (IRAP), social security, real estate and value-added tax, etc. Although the corporate tax rate of 24% is comparable to the average statutory corporate tax rate in other OECD countries, there are many additional items in the overall tax requirements.
The second is the regulatory differences in different regions. In Italy, local regulations and procedures vary from city to city, as it is the local authorities that decide how to implement national laws and regulations. For example, according to the EU Business Environment, it takes 860 days to resolve business disputes in Turin. By contrast, it takes twice as long to settle disputes in Reggio Calabria.
In addition, Italy is very inefficient in dealing with commercial disputes. It is understood that although Italy has made many improvements in the filing and process service procedures of its commercial litigation, the average time for resolving commercial disputes in Italy is still 1120 days, the average time for submitting and serving is 10 days, the average time for hearing and judgment is 840 days, and the average time for executing is 270 days.

Hot track
To sum up, in addition to the fashion field, Italy has also begun to vigorously promote digital development under the influence of Industry 4.0. According to the data of Eurostat in 2019, Italy had more than 5400 high-tech manufacturing enterprises at that time. In terms of the production and use of industrial robots, as well as cloud computing, Italy was also higher than the European average. In addition, at a time when the energy crisis has plagued global development, Italy is also vigorously developing the renewable energy industry.
Among them, in terms of industrial robots, although this field is still dominated by China, Japan, South Korea and the United States, Italy ranks first in the field of industrial robots in Europe, second only to Germany. It is understood that Italy ranks among the top ten in terms of the density of robots in the world. According to the data of the International Federation of Robotics, Italy has 185 robots for every 10,000 manufacturing employees, far ahead of Spain's 160, France's 132 and Britain's 71.
As cloud computing is one of the key technologies for national digital development, Italy has also accelerated the development of cloud computing technology and made certain achievements. According to Eurostat data, about 22% of Italian enterprises have used cloud technology, slightly higher than the European average of 21%, and higher than Spain's 18%, France's 17% and Germany's 16%. According to the statistics of the Milan Polytechnic University, the Italian cloud technology market grew by 18% in 2017, reaching a value of nearly 2 billion euros.
In terms of new energy, Italy's Ministry of Economic Development (MISE) released the country's new energy strategic plan (Strategy Energetica Nazionale SEN) for the period 2020-2030 in 2017. The plan points out that Italy will vigorously develop solar energy and renewable energy in the next decade, and gradually eliminate the share of coal power production by 2025. The Italian government expects that the share of renewable energy will increase from about 17.5% in 2017 to 27% in 2030.
Investment
Speaking of investment, in recent years, Italy's venture capital market is becoming more active. Ernst&Young's venture capital analysis report shows that in 2020, Italian start-ups will raise 569 million euros, a year-on-year increase of 55%, the best performance in five years.
In addition, according to the statistics of investment analysis platform Tracxn in 2021, there are 73 accelerators and incubators in Italy, including Digital Magics, PoliHub, Luiss Enlabs, UniCredit Start Lab, etc. In addition, according to VC Snapshot statistics of Growth Capital, CDP Venture Capital is the most active investor in Italy in 2020, followed by Italian Angels for Growth.
According to the 2020 French Science and Technology Venture Capital ReportIn 2020, the total financing amount of European start-ups only increased by 2%, Italy and Britain also increased by 2% year on year, France by 9%, and Germany by 7%.
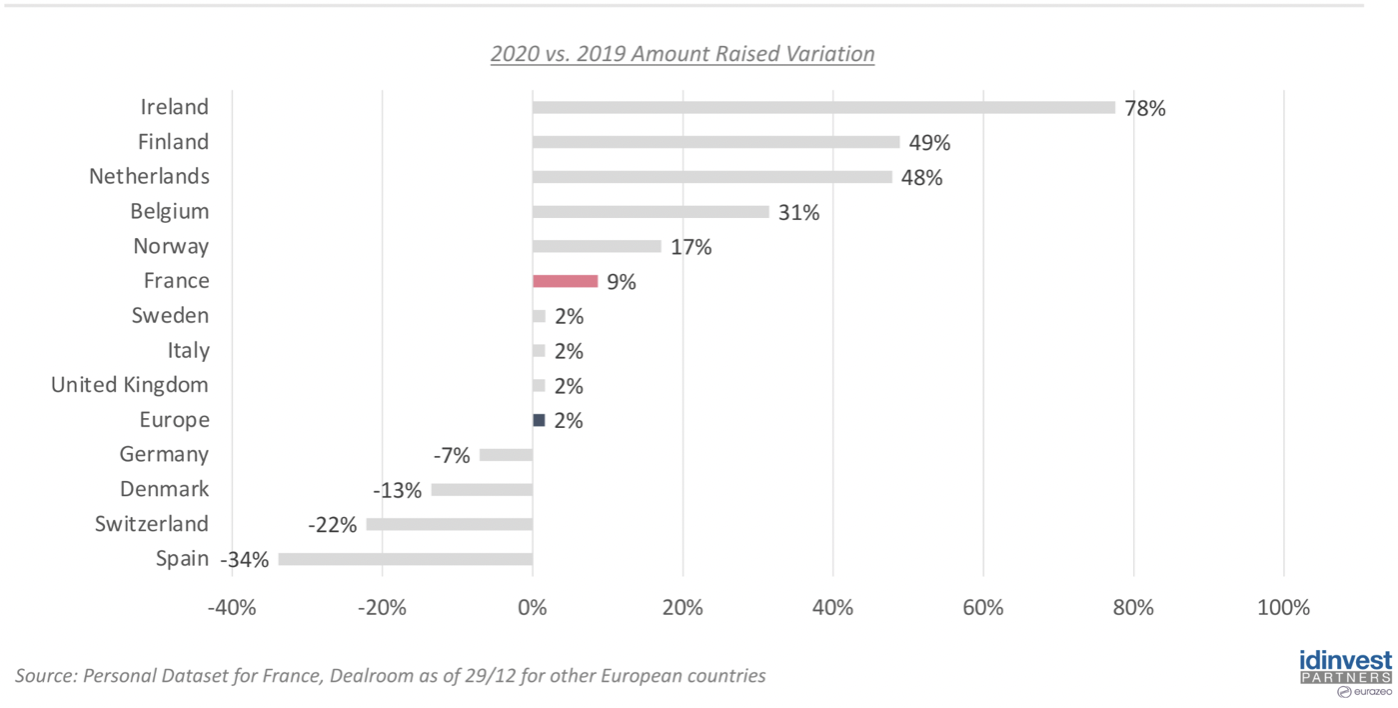
In terms of foreign direct investment (FDI), Ernst&Young's European Attraction Survey report shows that despite the spread of the COVID-19 in 2020, Italy's attraction to foreign investment is still further strengthened, and foreign countries care more about direct investment than most European countries. According to statistics, foreign investment in 113 new projects will increase by 5% year on year in 2020, while foreign direct investment in Europe as a whole will decrease by 13%. Foreign investment in Italy accounts for 2% of the total foreign investment in Europe, ranking 12th. The main investment comes from Europe and the United States, of which the United States accounts for 24%, France accounts for 16%, Germany accounts for 12%, and the United Kingdom accounts for 9%. In addition, China accounts for about 4%. Foreign direct investment is concentrated in the northwest (58 per cent) and central (24 per cent), as well as some areas with complete infrastructure and dense population.
Chinese enterprises and capital
In recent years, many Chinese capital have invested in Europe, and Italy is a very important destination. For Chinese enterprises and investors, in addition to establishing centers or branches in Italy, it is also a common way to layout Italy through acquisition or merger.
According to the Guidelines for Business Environment in Countries (Regions) where Enterprises Invest Abroad, Italy (2020), according to the data of the Ministry of Commerce, Chinese enterprises' investment in Italy covers finance, machinery manufacturing, energy and electricity, commercial trade, ocean transportation, information communication and other fields.
In terms of finance, Bank of China and Industrial and Commercial Bank of China established branches in Milan in 1998 and 2011 respectively; In the automotive field, Chang'an, Jianghuai and Qianjiang Motorcycles have all invested in Italy; In terms of renewable energy, there are CECEP and Hanergy Holding. In addition, Huawei and ZTE have also entered the field of information and communication early. Among them, the CEO of Huawei Italy said in 2019 that he would invest $3.1 billion in Italy in the next three years and create 1000 jobs in Italy.
With a long history, culture and geographical advantages, Italy has now become a manufacturing power and a gathering place for fashion and luxury brands. However, in terms of venture capital, Italy is still a "young man" who needs to catch up with all efforts.
In fact, in the past few years, 36Kr Global, Asia's leading new business media and enterprise service platform, has helped Asia's innovation capabilities cross national borders and be applied and tested in more markets by mobilizing ecological resources and service experience across Asia. In 2021, in order to provide the value of connectivity in a wider geographical scope,36Kr Global established the European Station KrEurope and Australia New Zealand Station Kr ANZ, aiming to help more Asian companies expand markets in Europe, Australia and New Zealand together with local partners, and help overseas companies enter Asia to promote business cooperation in Asia and overseas regions in a wider geographical scope.If your company is interested in cooperation, please contact zhaoxiaochun@36kr.com Detailed consultation.
Wen | Deng Yunxi
Editor | Zhao Xiaochun
