At the moment when the dividend of domestic Internet has peaked, more and more Chinese entrepreneurs and investors have begun to pay attention to "globalization". In 2021, 36 krypton will go to seaContinue to launch globalization manualTo explain the basic features, cultural environment, market characteristics and entrepreneurial opportunities of various countries in the European market one by one.
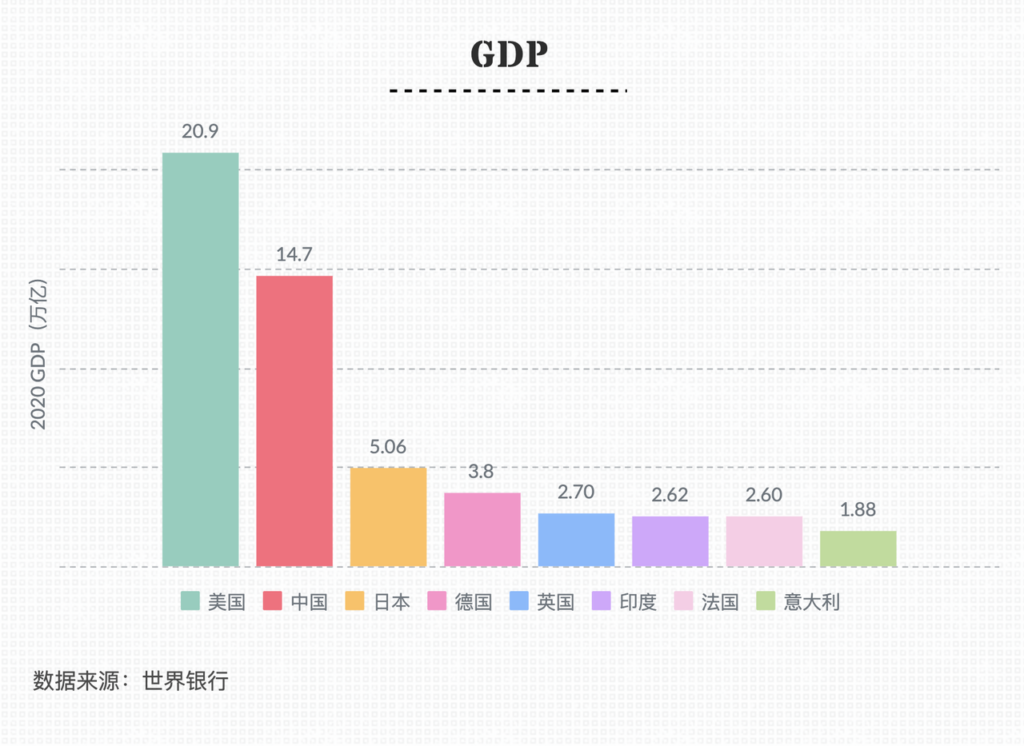
Germany is the largest economy in Europe, with its GDP ranking fourth in the world. After the Brexit of the UK, Germany will play a decisive role in the EU market. Germany is famous for its manufacturing industry worldwide and is the first to propose the concept of Industry 4.0. What inspiration can its scientific innovation market provide us?
The German chapter of the globalization manual will provide a general overview of Germany from the perspectives of history, humanities, education, etc., and introduce Germany's economy and venture capital ecology.
Basic information of the country
Geographical Environment and History
Germany is one of the largest countries in Europe, geographically located in the middle of Europe, bordering Denmark, the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, France, Switzerland, Austria, the Czech Republic and Poland.
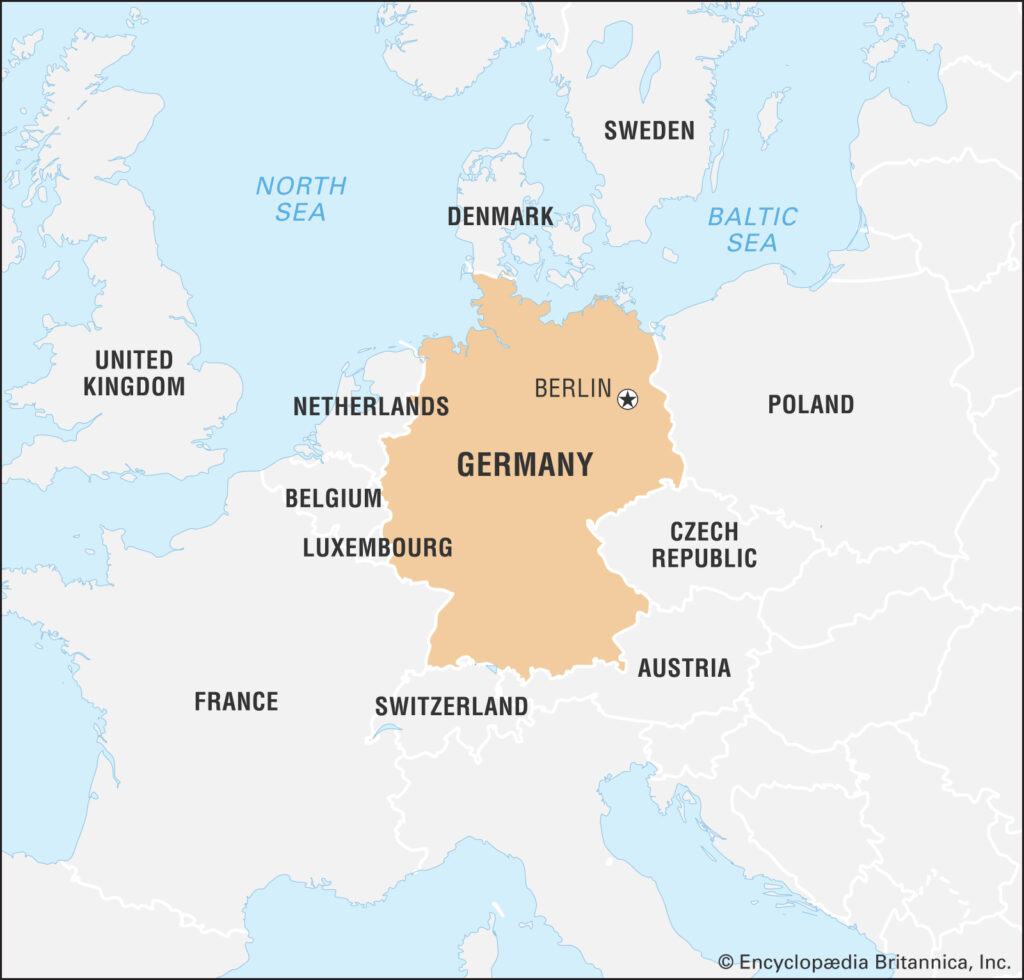
The full name of contemporary Germany is "Bundesrepublik Deutschland", the capital of Berlin. The past of two world wars, division and reunification still affects today's Germany.

Population and age
Germany consists of 16 federal states, with an existing population of 83 million (including foreign nationality). According to the World Bank, the urban population is 64 million, accounting for 77% of the total population, slightly higher than the EU average of 74.9%.
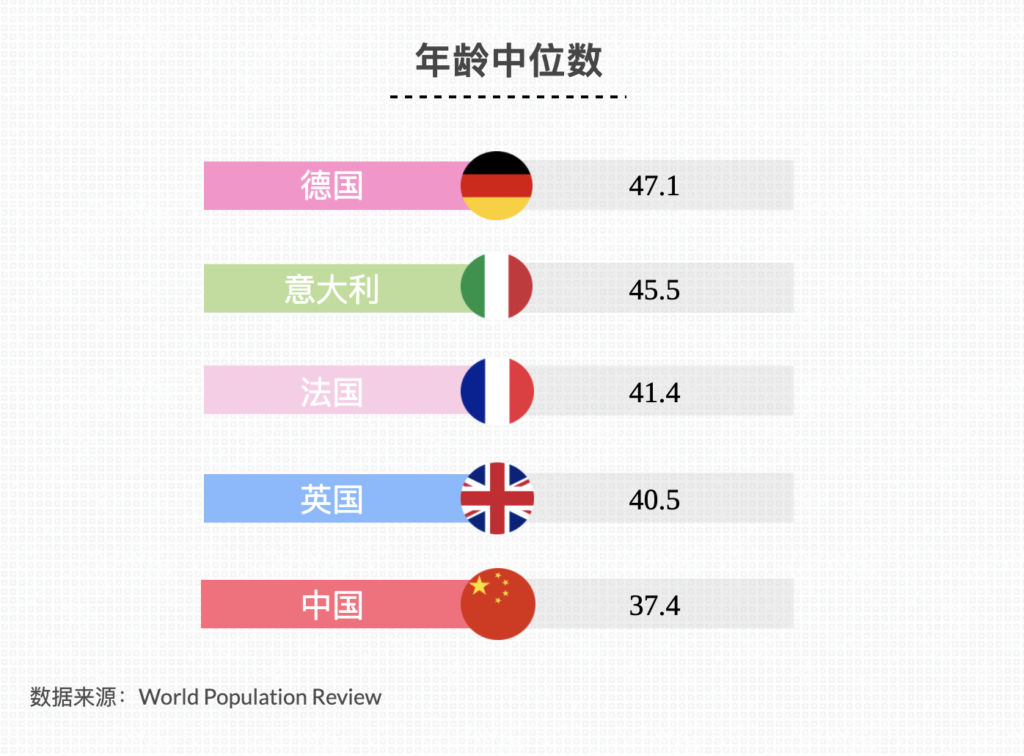
Germany has a high degree of population aging. According to the data of World Population Review in 2021, the median age of Germans is 47.1; According to the data of the World Bank, the proportion of people over 65 years old in Germany is 21.7%, that in the United States is 16.6%, and that in China is 11.9%.
education
The education systems of German states are different, which can be roughly divided into primary education, secondary education and higher education. Among them, secondary education mainly includes Gymnasium, Gesamtschule, Realschule and Hauptshule, the latter two are vocational education oriented; Higher education institutions include universities (University ä ten), professional schools (Fachhochschulen) and music and art schools.
Germany has a high degree of education popularization and education level. In the 20-24 age group, 53% of people have higher education admission qualifications. German higher education institutions are mostly public, and undergraduate courses and most master's courses are free of tuition.
Germany's vocational education system is also recognized. Germany has a "dual track" learning program (VET), which combines degree learning with professional practice. Students also work in enterprises as apprentices during their schooling. After finishing their studies, they obtain diplomas and vocational qualification certificates, and about 70% of them are retained by enterprises. Under this system, the unemployment rate of youth aged 15-24 in Germany is 7.5%, which is only higher than that of the Czech Republic in EU countries.
Language and Religion
The official language of Germany is German, and more than 95% of Germans are native speakers of German. German is also widely used in Central Europe. In addition to Germany, it is also the official language of Austria, Switzerland, Belgium, Luxembourg and Liechtenstein.
According to the data of the Global Religious Future Project, 66% of German people are Christians, 6.9% are Muslims, and 26.3% do not belong to any religion.
Politics
Germany is a parliamentary republic, and the legislative power belongs to the parliament. The Head of State is the President, who only plays a symbolic role. The head of government is the Prime Minister, who is nominated by the President and elected by a majority vote of the Parliament, and is responsible for leading the government and formulating policies. Since the reunification of Germany, the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) and the German Social Democratic Party (SPD) have been the two major political parties in Germany. Since 2005, Angela Merkel has been elected as German Chancellor consecutively. Angela Merkel, who has been in power for 16 years, is a member of the Christian Democratic Union. Olaf Scholz, the Social Democrat, will succeed Merkel. It is reported that she is expected to take office formally in December.
Economic Situation&Entrepreneurship Ecology
Economic overview
When it comes to the European economy, Germany is a pillar that cannot be ignored. Germany is the largest economy in Europe, with GDP ranking fourth in the world and first in Europe. The income level of Germany is relatively high. According to the data of the World Bank, the per capita GDP of Germany in 2020 will be 46208 US dollars, which is higher than the EU average of 34114 US dollars.
The income gap in Germany is also small. According to OECD data, the Gini coefficient in 2018 is 0.289 (1=income inequality, 0=income equality), and the income gap is smaller than that in Canada and France.
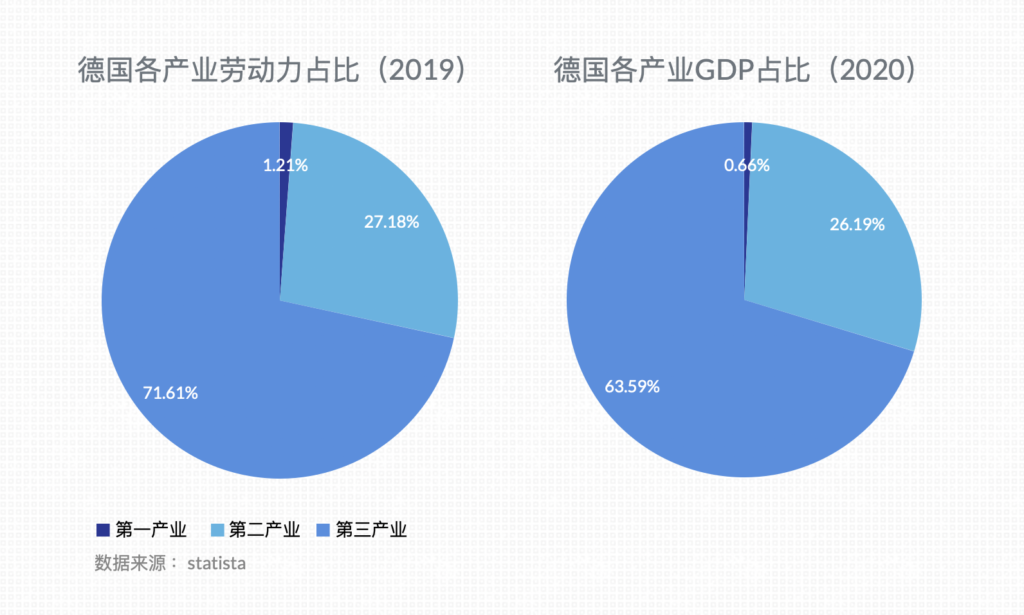
Germany is a big manufacturing country with a world-renowned manufacturing brand, including world leading automobile manufacturers such as Audi, BMW, Daimler, Volkswagen, and well-known electrical equipment manufacturers such as Siemens and AEG. In addition to machinery manufacturing, automobile and electrical engineering, Germany's important industries also include chemical industry, food processing, etc.
In 2020, affected by the economic downturn at the initial stage of the epidemic, Germany's imports and exports recorded the largest year-on-year decline since the financial and economic crisis in 2009. However, China remains Germany's largest trading partner, with bilateral trade volume reaching 212.1 billion euros. China's exports to Germany mainly include data processing and electronic optical equipment, electrical equipment, clothing, mechanical equipment, metal products, etc. China's imports from Germany mainly include automobiles and accessories, mechanical equipment, data processing and electronic optical equipment, electrical equipment, chemical products, etc.
Foreign investment
Germany is generally open to foreign investors. From 2020 to 2021, Germany willForeign Direct Investment Confidence IndexIt ranks third in China after the United States and Canada. Issued by the World BankBusiness Environment Report 2020In China, Germany's business environment ranks 22nd among 190 economies.
However, in the past two years, German laws and regulations on foreign investment have been revised many times, requiring that foreign investment in some fields be subject to mandatory declaration, including key infrastructure (energy, IT and telecommunications, food, etc.), specific medical care (such as PPE), and key technologies (artificial intelligence, robots, semiconductors, etc.). Based on the Foreign Trade and Payment Law and the Foreign Trade Regulations, the Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs and Energy of Germany has the right to review the acquisition of German companies by foreign companies.
according toChina's 2020 Foreign Direct Investment BulletinIn 2020, China invested 12.69 billion dollars in Europe, of which Germany accounted for 1.38 billion dollars, ranking behind the Netherlands and Sweden. Issued by the German Federal Foreign Trade and Investment AgencyReport on Foreign Enterprises' Investment in Germany in 2020It shows that there will be 1684 foreign direct investment projects settled in Germany in 2020 (including green land investment, expansion and relocation, excluding mergers and acquisitions), a decrease of 9% compared with 2019. Among them, the number of Chinese investment projects in Germany was 170, ranking third, second only to the United States (254 projects) and Switzerland (219 projects), with a year-on-year growth of 10% (154 projects in 2019).
According to the report, the main industries invested by Chinese enterprises are machinery manufacturing and equipment (14%), consumer food (13%), electronics and semiconductor industry (12%), health pharmacy and biotechnology (11%), business and financial services (11%), and information and communication technology and software (10%). The areas in which Chinese enterprises invest the most are sales and market support (42%), manufacturing and R&D (19%), retail (17%) and commercial services (9%).
Entrepreneurship Ecology
By contrast, the German venture capital market is still young. In 2020, German start-ups attracted a total of 6.4 billion euros (about 7.5 billion dollars) of venture capital, an increase of 20% over the previous year. In the same year, the UK figure was 15 billion dollars. According to KfW data, German venture capital accounted for about 0.047% of GDP in 2017-2019, while the UK accounted for about 0.1%.
Thanks to numerous federal and state public capital projects, German start-ups at the initial stage can obtain more local capital support, but the follow-up is weak. As enterprises grow, overseas investment accounts for a larger proportion. The seed round and A round investments of German start-ups are mostly led by local investment institutions,According to KfW,Half of them are led by foreign investors, only 5% are led by German investment institutions, and 45% are mixed domestic and foreign investors.
Under the impact of the epidemic in 2020, the German federal government has set up a "future fund" of 2 billion euros in the German Credit Bank of Renaissance to finance start-ups and activate the venture capital market(Future Fund), covering all stages of the development of start-up enterprises. Later, it plans to add another 10 billion euros to the fund.
Specific to the region, according toReport on Science and Technology Venture Capital Investment in German speaking Area 2021Referring to the data of Invest Europe, Germany and its main cities Berlin and Munich have been among the regions with the fastest capital growth since 2007. From 2007 to 2015, the proportion of European venture capital funds flowing into Berlin alone increased from 2.4% to 8%. By 2020, Berlin and Munich will be the third and fourth largest European cities in terms of financing amount, respectively, behind London and Paris.
Active investment institutions
PitchBook has counted the 10 most active German venture capital institutions since 2014 by the number of investments in 2019, as follows (the number of investments in brackets is the number of investments at the time of statistics):
- High Tech Gr ü nderfolds (284), seed investment of high-tech start-ups
- Global Founders Capital (155), seed and growth investment
- HV Holtzbrinck Ventures (116), investment in retail, FMCG, software and infrastructure
- Point Nine Capital (113), B2B SaaS and B2B e-commerce seed investment
- Earlybird Venture Capital (103), investing in European scientific and technological innovation
- Rocket Internet (98), investing in Internet and technology enterprises
- Btov Partners (95), investing in early stage enterprises, headquartered in Switzerland
- IBB Beteiligungsgesellschaft (86), investing in seed wheel, early stage and late stage enterprises
- Deutsche Telekom Capital Partners (82), part of Deutsche Telekom
- Project A (77), investing in early stage enterprises
Ernst&Young's Report on German Venture Capital and Startups in 2020Some well-known investment institutions active in Germany are also listed in:
- LGT Lightstone (UK) focused on influence investment, led investment in Infirm's 170 million US dollars round C financing, and co invested in Lithium Aviation;
- Atomico (UK) Phase V Fund of $820 million is one of the largest venture capital funds in Europe, leading the investment of $60 million in round B financing in Scoutbee, and participating in investment in Lilium and Infarm;
- Index Ventures (USA), led the investment in Raisin D-round financing in 2019, and participated in three of the top 100 financing rounds in 2020: Personio, Taxfix, Cargo.one;
- Earlybird (Germany) has made more than 30 investments in 2020, including Isar Aerospace, Getsafe and Simscale;
- Tencent (China) will lead a US $100 million round D financing of N26 in 2020 and a US $81 million round C financing of Clark in 2021;
- Redalpine (Switzerland) has made tens of millions of investments in German companies in 2020, including Taxfix and Zenjob.
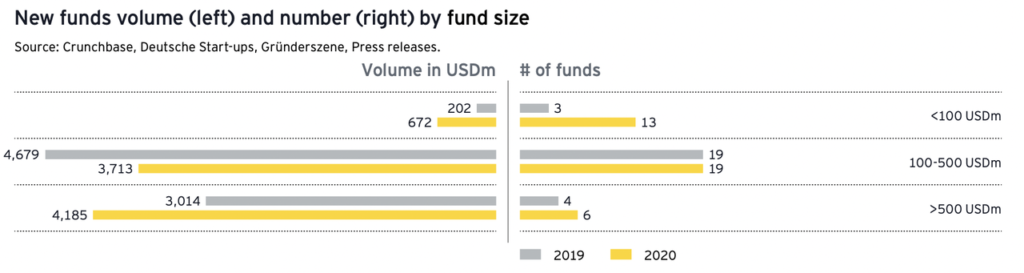
Hot track
In September 2018, the German Federal Government issued the High tech Strategy 2025, which focuses on 12 fields, including health care, energy conservation and environmental protection, intelligent transportation, urban and rural, safety, economy and labor 4.0, and promises to increase the proportion of scientific research and innovation investment in GDP to 3.5% by 2025.
According to Ernst&Young's German Venture Capital and Startups in 2020,Financial technology, mobility, software&analytics are the hot tracks of German venture capital. In recent years, the B2B model has also attracted increasing attention. In 2020, 40 of the 100 start-ups with the largest cumulative financing will be B2B service providers, obtaining a total of 4.1 billion dollars in financing. Price f (x), Personio, LeanIX, Contentful and other enterprises have completed a financing round of more than 50 million dollars in 2020.
E-commerce and food distribution have gained development opportunities during the epidemic. Gorillas in Berlin received $45 million in seed round financing. Amazon M&A operating companies such as SellerX and Razor Group have established a "buy and build" model to acquire Amazon sellers and promote growth. The epidemic also exposed the shortcomings of the digitalization of the medical system and increased the interest of venture capital in health technology. 12% of the financing rounds were invested in digital medical start-ups. Five companies, including PlusDental, Kaia Health and Temedica, received more than 20 million dollars of investment.
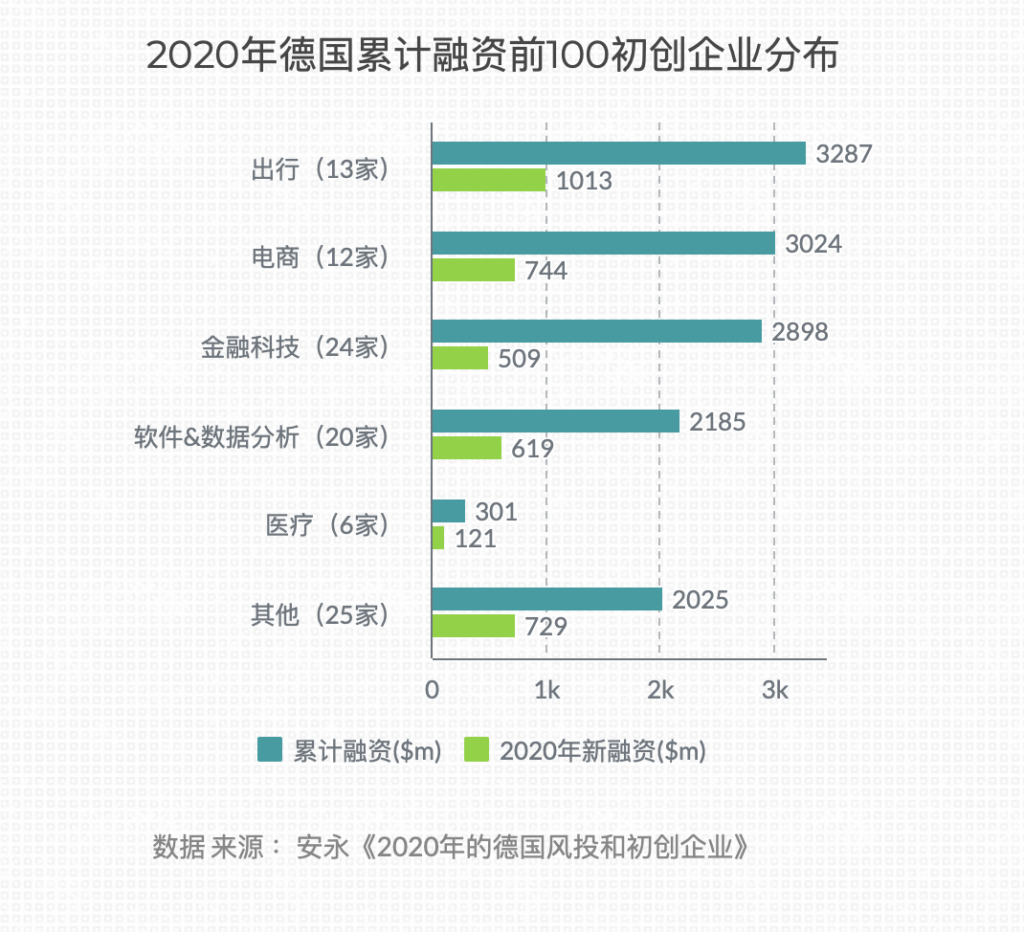
Big companies and unicorns
Among the world's top 500 enterprises, 29 are German enterprises, including Volkswagen, Daimler, Allianz, BMW, Siemens, Bosch, SAP, etc.
According to CB Insights data, there are currently 21 Unicorn enterprises in Germany (November 2021), 13 of which will be newly promoted in 2021; There are 6 companies in the field of financial technology.
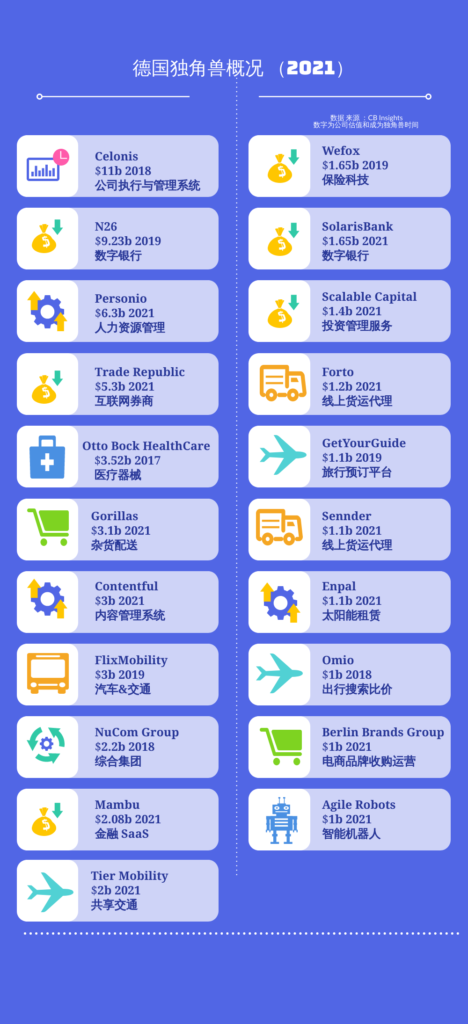
As the hometown of famous auto brands such as Audi and Mercedes Benz, it also attracts Tesla to set up a super factory. Germany, an ancient and young manufacturing country, has broad development space for its entrepreneurial ecology.
After introducing Germany, the next stop of the globalization manual will continue to go to France, the "free entrepreneurial country". Please look forward to it.
In fact, in the past few years, 36Kr Global, Asia's leading new business media and enterprise service platform, has helped Asia's innovation capabilities cross national borders and be applied and tested in more markets by mobilizing ecological resources and service experience across Asia. In 2021, in order to provide the value of connectivity in a wider geographical scope,36Kr Global established the European Station KrEurope and Australia New Zealand Station Kr ANZ, aiming to help more Asian companies expand markets in Europe, Australia and New Zealand together with local partners, and help overseas companies enter Asia to promote business cooperation in Asia and overseas regions in a wider geographical scope.If your company is interested in cooperation, please contact zhaoxiaochun@36kr.com Detailed consultation.
Article | Shi Yi
Editor | Zhao Xiaochun
